
- ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING HOW TO
- ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING INSTALL
- ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING ANDROID
- ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING SOFTWARE
- ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING SIMULATOR
ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING ANDROID
Step 3 - Set up Cordova, Android and your Windows environment Go ahead and follow or select your own preferences. Most of the options given by the CLI are default options.
ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING INSTALL
Step 1 - Install Quasar CLI and create a project in the folder "myquasar" npm install -g create myquasar I also assume that you already have some Vue knowledge.
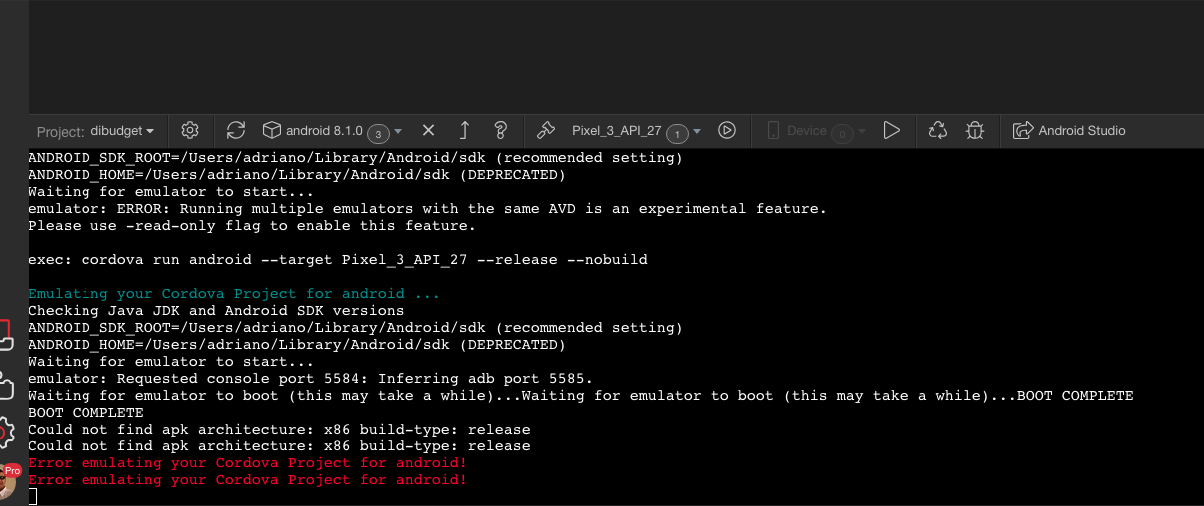

Hopefully this tutorial will help someone get started in developing mobile apps. Here I will outline my notes and any difficulties I encountered along the way during my own set up.
ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING HOW TO
Note that the Quasar website already has quite good documentation on how to get started. In this introduction I'll provide an overview on how to build a simple Android app. Using Machine Learning on the top of the checks might also aid in getting more accurate results from a mobile emulator detector.Quasar is a Vue framework that makes it easy to build hybrid mobile apps using Cordova. However, it may prove to be difficult because of the great number of different emulators and hence, an important margin of error, that create important False Acceptance Rate or important False Reject Rates. There are many more detection techniques available than have been described here. Detecting an emulator in an Android or iOS context is not per se the most difficult challenge for a RASP system. Additionally, an analysis of TTL (Time to Live/Hop limits) values can also give some clues, as shown in the following table: The MAC addresses of the network cards may have specific values. Networking Environment ChecksĪ network can give a lot of hints that an emulator is present. The same can be done with the IMSI check, etc. So by using that table with known values of a real device, we can eventually decide if we are dealing with an emulator or notĪdditionally, an IMEI check will return a value of ‘000000000000000’ for an emulator. For each emulator, we list the default values. The following table gives an overview of such possibilities. It is possible to detect the presence of an emulator by looking at inconsistencies with the hardware.
ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING SIMULATOR
Here we list the different default values for several popular emulators: BlueStacks, GenyMotion, Andy, YouWave, and ARCWelder.īy themselves, these values can create a simulator fingerprint. Reading the build values may be a quick test to check for an emulator.Īll the following values can be accessed programmatically on Android, and they often contain proof of the presence of an emulator. Most of the detection techniques are based on the presence of such artifacts, which can be located in the file system, in the network, or in the hardware. But it still has artifacts that betray its presence. Therefore, several proprietary checks have to be done by the RASP system.Īn emulator reproduces, with great fidelity, the behavior and functioning of the original operating system. There is no official API in iOS or Android to detect an emulator. A simulator acts more as a ‘stub’ system that mimics rather than emulate (hence the name). A hypervisor can be seen as “in-between” a virtual machine and an emulator. A virtual machine relies on a real CPU to perform virtualization.
ANDROID EMULATOR MAC CORDOVA NOT RUNNING SOFTWARE
An emulator, ‘emulates’ the whole system, including the processor, in software (which means that it is often very slow). There are differences between an emulator, a virtual machine, a hypervisor, and a simulator. This article mainly looks at a number of techniques for detecting Android emulators.Īs we shall see, there are many ways to detect emulators, but there are also a great number of such emulators on the market and counting! Android and iOS Emulators Often-used Android emulators include: In order to prevent a mobile app from running on an emulator, effective emulator detection must first be in place. Whatever an attacker wants to do: reverse the code, attach a debugger, tamper the application, etc., the first step is usually to use an Android or iOS emulator.Īn important role of Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) mechanisms is, therefore, to prevent the protected application from running inside an emulator (simulated environment). Attacks against mobile banking & payment applications often start by using an emulator for the mobile operating system where the targeted application will be run and analyzed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
